
You wonder if you should activate the cath lab, or if a bedside echo might help.Īn 82-year-old woman presents to the ED with chest pain. His ECG shows 4-mm anterior ST-segment depressions. Chest x-ray confirms your clinical suspicion of pulmonary edema. He has bibasilar crackles and visibly increased work of breathing. His heart rate is 110 bpm and blood pressure is 90/40 mm Hg. He has a history of hypertension, diabetes, and coronary artery disease, with baseline stable angina. He also notes dyspnea and lightheadedness. However, the pain didn’t resolve with rest and has been worsening since onset, and is currently 9/10 in severity. Initially, it felt similar to his usual episodes of angina, with left-sided pressure radiating to his left arm. Your intern asks if she can go home since her troponin is low and she looks well.Ī 69-year-old man presents to the ED with chest pain that began an hour prior to presentation, while he was walking home from the store. Her ECG shows nonspecific ST-segment flattening, and her initial troponin is 0.09 ng/mL (reference range, 0-0.04 ng/mL). In the ED, her vital signs are within normal limits and her exam is unremarkable. Her only past medical history is hypertension. The pain is located in the center of her chest, and she describes it as a “pressure” sensation. Two hours prior to ED arrival, she was doing yard work and developed chest pain that was much more severe. She said that for the past month she has been getting short of breath more easily on her daily walks, with occasional discomfort in her chest, requiring her to stop and rest. Opening CasesĪ 76-year-old woman presents to the ED with chest pain. Issues surrounding special patient populations are addressed, and new diagnostic and therapeutic modalities are discussed. In this review, current national management guidelines for NSTEMI are summarized as they pertain to the ED, and the evidence base supporting them is considered. Non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is twice as common as ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), and lack of clarity surrounding the best management of this condition can contribute to adverse outcomes. A quarter of these patients will be diagnosed with acute coronary syndromes, but among those, nearly half will have nondiagnostic electrocardiograms. Anterior STEMI on ElectrocardiogramĬhest pain is the second most common complaint in emergency departments, with 6.4 million visits annually in the United States. HEART Score for Suspected Acute Coronary Syndromesįigure 1. Clinical Features of Type 1 and Type 2 Myocardial Infarction American Heart Association/ American College of Cardiology Classes of Recommendation and Levels of Evidence Risk Management Pitfalls for Management of NSTEMI in the Emergency DepartmentĬlinical Pathway for Risk Stratification for STEMI and NSTEMI in the Emergency DepartmentĬlinical Pathway for Management of NSTEMI in the Emergency Department.Ischemia-Guided Strategy Versus Early-Invasive Management StrategyĬopeptin as a Biomarker for Acute Coronary Syndromes Left Bundle Branch Block and Sgarbossa Criteria
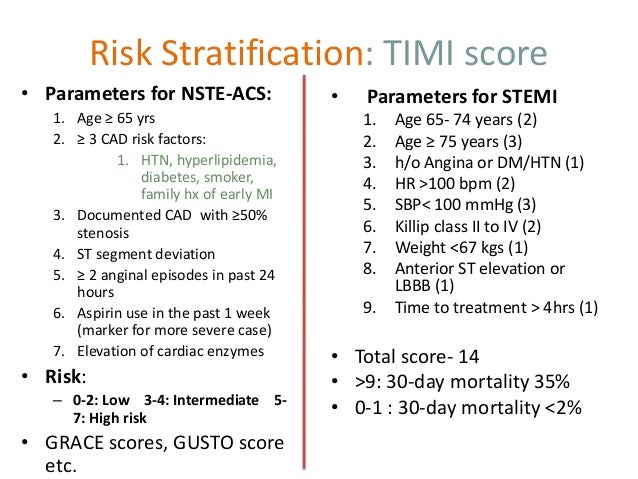
What is the best ED management when you don’t know whether the patient’s further treatment strategy is going to be early-invasive or ischemia-guided? Is there new evidence on treatment strategies – analgesia, antiplatelets, anticoagulation? Risk stratification scores: HEART, GRACE, TIMI: Which is best for the ED? What is the latest evidence on the value of high-sensitivity troponin assays? How has the modified Sgarbossa criteria increased sensitivity for identifying MI?
Timi score for stemi serial#
What is the sensitivity of serial ECGs in detecting an occluding lesion? What are the different causes of STEMI and NSTEMI? Type 1 MI versus type 2?īesides chest pain, what is the likelihood that other symptoms, such as nausea, dyspnea, and diaphoresis, are pointing to MI? Are these related to age, ethnicity, and sex? What are the ECG criteria that differentiate STEMI and NSTEMI?
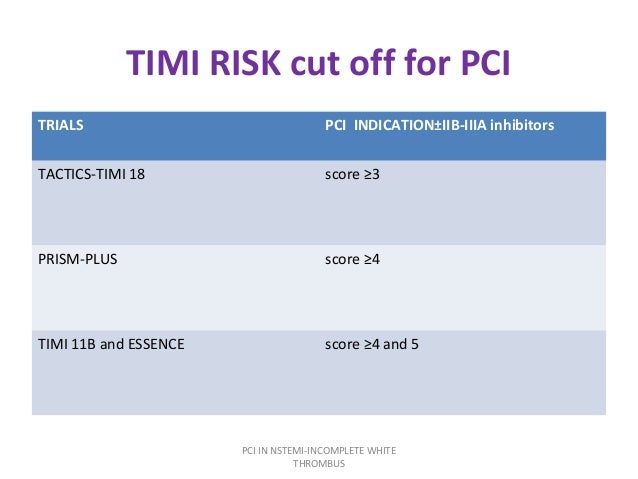
For the emergency clinician, it is critical to make the correct diagnosis, fast: STEMI, NSTEMI, unstable angina (or is it pulmonary embolism or just heartburn?). Up to 25% of patients who present to the ED with chest pain are diagnosed with acute coronary syndromes (ACS).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
